38 in supervised learning class labels of the training samples are known
PDF Supervised Learning: Classificaon - fenyolab.org • The known label of test sample is compared with the classified result from the model • Accuracy rate is the percentage of test set samples that are correctly classified by the model • Test set is independent of training set (otherwise over-fing) • If the accuracy is acceptable, use the model to classify new data ML | Types of Learning - Supervised Learning - GeeksforGeeks Supervised learning is when the model is getting trained on a labelled dataset. A labelled dataset is one that has both input and output parameters. In this type of learning both training and validation, datasets are labelled as shown in the figures below. Both the above figures have labelled data set as follows:
120 questions with answers in SUPERVISED LEARNING | Science topic Dear N. Janardhan. Supervised learning is a machine learning method distinguished by the use of labelled datasets. The datasets are intended to train or "supervise" computers in properly ...

In supervised learning class labels of the training samples are known
6. Learning to Classify Text - Natural Language Toolkit 1 Supervised Classification. Classification is the task of choosing the correct class label for a given input. In basic classification tasks, each input is considered in isolation from all other inputs, and the set of labels is defined in advance. Some examples of classification tasks are: Deciding whether an email is spam or not. supervised learning and labels - Data Science Stack Exchange The main difference between supervised and unsupervised learning is the following: In supervised learning you have a set of labelled data, meaning that you have the values of the inputs and the outputs. What you try to achieve with machine learning is to find the true relationship between them, what we usually call the model in math. Supervised Learning - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The procedure of Supervised Learning can be described as the follows: we use x(i) to denote the input variables, and y(i) to denote the output variable. A pair ( x(i), y(i)) is a training example, and the training set that we will use to learn is { ( x(i), y(i) ), i = 1, 2, …, m }. ( i) in the notation is an index into the training set.
In supervised learning class labels of the training samples are known. Types Of Machine Learning: Supervised Vs ... - Software Testing Help Supervised learning is learning with the help of labeled data. The ML algorithms are fed with a training dataset in which for every input data the output is known, to predict future outcomes. This model is highly accurate and fast, but it requires high expertise and time to build. Also, these models require rebuilding if the data changes. Supervised learning - Wikipedia Supervised learning (SL) is the machine learning task of learning a function that maps an input to an output based on example input-output pairs. It infers a function from labeled training data consisting of a set of training examples . [2] PDF Supervised and Unsupervised Learning - Astronomy Supervised Learning • Training data includes both the input and the desired results. • For some examples the correct results (targets) are known and are given in input to the model during the learning process. • The construcon of a proper training, Supervised and Unsupervised Learning in Data Mining The difference is that in supervised learning the "categories", "classes" or "labels" are known. In unsupervised learning, they are not, and the learning process attempts to find appropriate "categories". In both kinds of learning all parameters are considered to determine which are most appropriate to perform the classification.
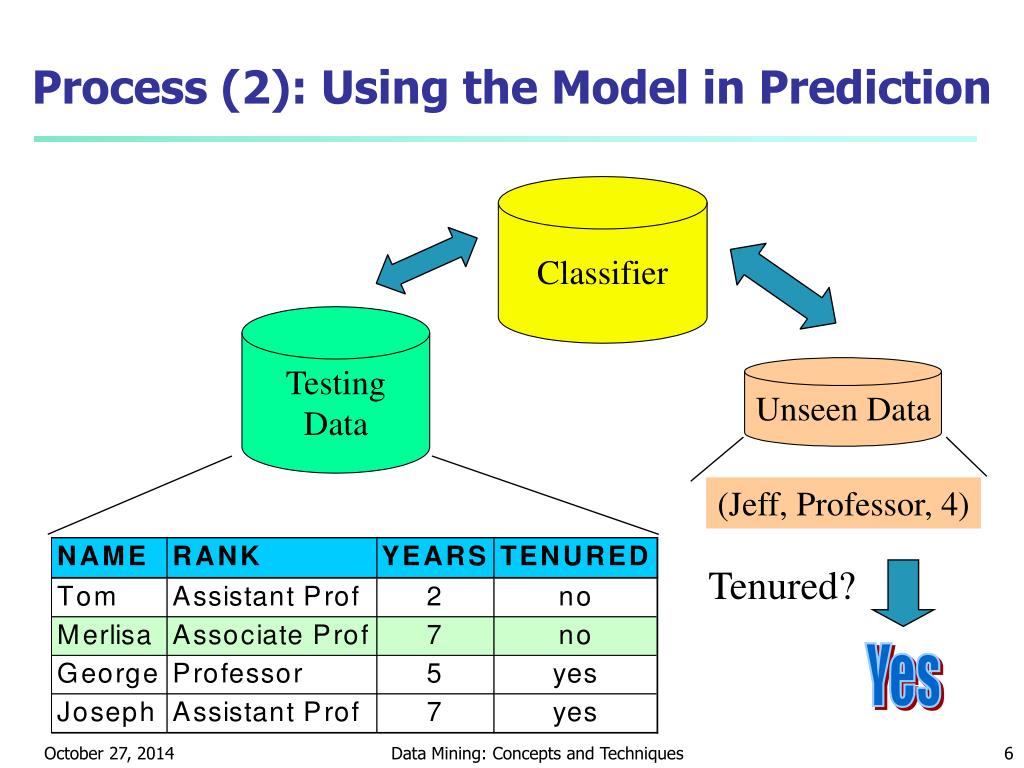
Semi-Supervised Learning With Label Propagation Semi-supervised learning algorithms are unlike supervised learning algorithms that are only able to learn from labeled training data. A popular approach to semi-supervised learning is to create a graph that connects examples in the training dataset and propagate known labels through the edges of the graph to label unlabeled examples. Edward - Supervised Learning (Classification) Supervised Learning (Classification) In supervised learning, the task is to infer hidden structure from labeled data, comprised of training examples \(\{(x_n, y_n)\}\). Classification means the output \(y\) takes discrete values. We demonstrate with an example in Edward. An interactive version with Jupyter notebook is available here. Data Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning Explained - Seldon Examples of supervised learning classification. A classification problem in machine learning is when a model is used to classify whether data belongs to a known group or object class. Models will assign a class label to the data it processes, which is learned by the algorithm through training on labelled training data. Clinical-grade computational pathology using weakly ... Current methods for weakly supervised WSI classification rely on deep learning models trained under variants of the MIL assumption. Typically, a two-step approach is used, where first a classifier is trained with MIL at the tile level and then the predicted scores for each tile within a WSI are aggregated, usually by combining (pooling) their ...
Basics of Supervised Learning (Classification) - Medium They are namely Learning and Querying phase. The learning phase consists of two components of namely Induction (training) and Deduction (testing). The querying phase is also known as application phase. Let's talk about it in a more formal way now. Formal definition: Improve over task T, with respect to performance measure P, based on experience E. PPT Supervised Learning - University of Illinois Chicago CS583, Bing Liu, UIC * Supervised vs. unsupervised Learning Supervised learning: classification is seen as supervised learning from examples. Supervision: The data (observations, measurements, etc.) are labeled with pre-defined classes. It is like that a "teacher" gives the classes (supervision). Test data are classified into these classes too. Semi-Supervised Learning With Label Spreading A popular approach to semi-supervised learning is to create a graph that connects examples in the training dataset and propagates known labels through the edges of the graph to label unlabeled examples. An example of this approach to semi-supervised learning is the label spreading algorithm for classification predictive modeling. An Introduction to Supervised Learning - Towards Data Science That is the most important thing — supervised learning has something that is called an expert label. That's a fancy word for meaning that it is labeled for an outcome; or for any given case, there is a known, desired outcome. Unsupervised learning (clustering) does not assume that it knows the answer.
Supervised Machine Learning: What is, Algorithms with Examples Supervised Machine Learning is an algorithm that learns from labeled training data to help you predict outcomes for unforeseen data. In Supervised learning, you train the machine using data that is well "labeled.". It means some data is already tagged with correct answers. It can be compared to learning in the presence of a supervisor or a ...
In supervised learning, class labels of the training samples are scouteo In supervised learning, class labels of the training samples are "known." The correct answer is "known." The other options for the question were "unknown," "partially known," and "doesn't matter." It cannot be "unknown," because training samples must be known.
Unstructured Data Classification.txt - In Supervised learning, class ... in supervised learning, class labels of the training samples are known select pre-processing techniques from the options all the options a classifer that can compute using numeric as well as categorical values is random forest classifier classification where each data is mapped to more than one class is called multi-class classification tf-idf is …
Zero-shot learning - Wikipedia Class-class similarity. Here, classes are embedded in a continuous space. a zero-shot classifier can predict that a sample corresponds to some position in that space, and the nearest embedded class is used as a predicted class, even if no such samples were observed during training. Generalized zero-shot learning. The above ZSL setup assumes ...
3 Examples of Supervised Learning - Simplicable A definition of supervised learning with examples. Supervised learning is an approach to machine learning that is based on training data that includes expected answers. An artificial intelligence uses the data to build general models that map the data to the correct answer. The following are illustrative examples.
What is Supervised Learning? | IBM What is supervised learning? Supervised learning, also known as supervised machine learning, is a subcategory of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It is defined by its use of labeled datasets to train algorithms that to classify data or predict outcomes accurately.
Supervised and Unsupervised learning - GeeksforGeeks Supervised learning, as the name indicates, has the presence of a supervisor as a teacher. Basically supervised learning is when we teach or train the machine using data that is well labelled. Which means some data is already tagged with the correct answer.
The Beginner’s Guide to Contrastive Learning Supervised Contrastive Learning (SSCL) vs. Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning (SCL) Supervised Learning refers to the learning paradigm where both the data and their corresponding labels are available for training a model. In Self-Supervised Learning, on the other hand, the model generates labels using the raw input data without any external ...






Post a Comment for "38 in supervised learning class labels of the training samples are known"